Acid Rain Definition:
Acid rain is any form of precipitation that is
unusually acidic (elevated level of hydrogen ions) due to anthropogenic gaseous
emissions in the atmosphere. Acid rain contains acidic components such as sulfuric
acid and nitric acid.
Brief History of Acid Rain:
Measuring Acid Rain: (How it can be determined if rain is acid
rain)
Acid rain is measured on
a pH scale. Acid rain is one of the most serious environmental problems that
emerged due to air pollution. Normal or unpolluted rainfall has a pH of 5.6
because carbon dioxide and water in the air react together to form carbonic
acid, a weak acid.
CO2 +
H2O............ H2CO3 (carbonic acid).
The term acid rain is applied to any type of precipitation with a pH level below 5.
Acid Rain Formation:
Acid rain is the consequence of air pollution. When moisture of air reacts with oxides of carbon, sulfur, and nitrogen in the atmosphere to produce a mixture of carbonic, sulfuric, and nitric acids.
Causes and Sources of Acid Rain:
- Anthropogenic activities are the main cause of acid rain which includes the burning of fossil fuel.
- The emission of gases from automobiles.
- Burning of coal from Power plant
- The emission of gases from industries
- Both Sulfur dioxide and Nitrogen dioxide are the major sources of acid rain formation.
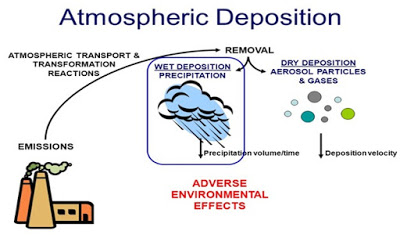
Dry and Wet Deposition:
Wet deposition refers to fog, acid rain, and snow. Wet deposition of acid rain affects a variety of plants and animals. Dry deposition refers to acidic gases and particles. Almost half of the acidity in the atmosphere falls back to the ground through dry deposition.







No comments:
Post a Comment