The effects of air pollution can be
categorized into the following types.
1) Impacts on Human Health
2) Impacts on Animals
3) Impacts on Plants
4) Impacts on Environment
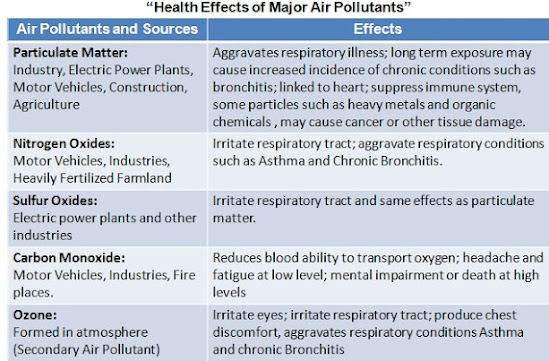
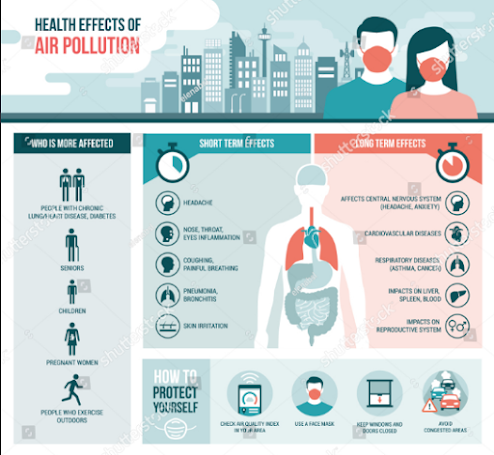
1) Impact on Human Health:
2- Impacts on Animals:
- Acid rain can harm fish and other wildlife.
- Chlorofluorocarbon (CFCs) depletes ozone layer. As a result, ultraviolet radiations can penetrate through the atmosphere and cause skin cancer, and damages plants and wildlife.
- Ozone molecules in the troposphere cause damaging effects on the lung tissues of animals.
3. Impacts on Plants:
- A higher level of sulfur dioxide is harmful to plants and kills leaf tissues.
- Nitrogen oxides cause the breakdown of plant tissues.
- Peroxyacetyl nitrates (PANs) have the highest toxicity to plants and attack younger leaves of plants.
- Acid rain causes direct and indirect phytotoxicity to plants.
- Acid rain causes depletion of nutrients cations (e.g. calcium and magnesium) from the soil. This results in reduced soil fertility and poor plant growth.
4. Impacts on Environment:
Particulate matter causes reduction and
distortion of visibility. Smog causes damage to the materials and reduces
visibility. Air pollutants react with one another and create acidic compounds.
These compounds cause adverse effects on buildings and vegetation.
- Greenhouse gases are the causes of climate change and global warming.
- Some air pollutants (e.g. CFCs) cause ozone depletion
- Acid rain causes corrosion of exposed structures, equipment, ornamental material, etc.





No comments:
Post a Comment