Introduction:
The term “greenhouse” was first used by Nils Gustaf Ekholm (Swedish meteorologist) in 1901. Greenhouse gases are surrounding the earth's atmosphere to prevent the loss of heat into outer space. These gases are essential to sustain life on earth.
The abundance of Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere due to
anthropogenic activities are dangerous to life on earth:
The global community is
facing the issue of increased concentration of greenhouse gases which have
ultimate repercussions on human life and our natural climate.
Greenhouse Gases: CO2, CH4, N2O, Water vapors, etc
The UN climate conference of Paris
agreed by I95 countries to reduce the emissions of CO2 and other greenhouse
gases. The aim was to limit the global temperature below 2 ºC (relative to
pre-industrial climate). According to Climatologists the increased
concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere due to human activities
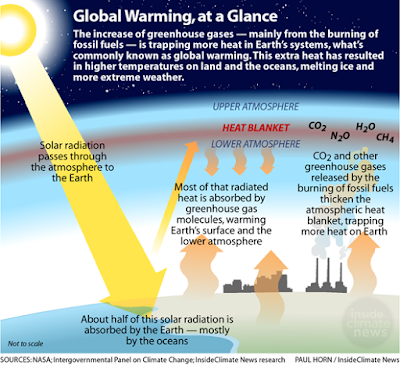
(burning of fossil fuel and deforestation) is warming the planet earth. These
gases act in a glass of a greenhouse which allows the sunlight to enter and
prevent the heat from escaping. The rise in atmospheric temperature is directly
related to an increase in anthropogenic emissions of greenhouse gases. Water
vapors, Methane, Carbon dioxide, Nitrous oxides, Ozone, and Chlorofluorocarbon
are the most abundant greenhouse gases in the atmosphere whereas
Chlorofluorocarbon is artificial gas. It is not found naturally in the
environment. The percentage contribution of greenhouse gases includes water vapors
(36-70%), carbon dioxide (9-26%), Methane (4-9%), Ozone (3-7%).
Impact of Greenhouse Gases on Environment:
- Impact on human life
- Global Warming
- Sea level rise
- Economic Impact
- Impact on Agriculture
- Effects on Aquatic system
- Effects on Hydrological Cycle
Control Measure of Greenhouse Gases:
- Financing low carbon energy
- Clean development mechanism
- Green energy portfolio standard
Following initiatives are mandatory to reduce the effects of
greenhouse gases:
- Conservation of energy
- Use of renewable energy
- Reforestation
- Methane gas recovery from solid waste
- Banning of CFC production
- National standards of pollutants
- International conferences and seminars





No comments:
Post a Comment