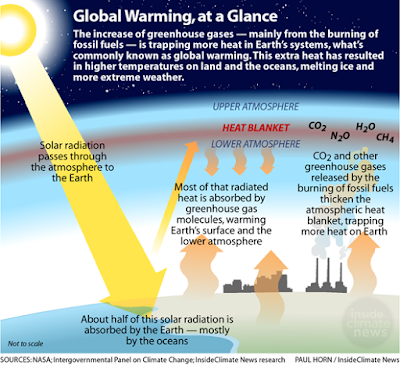
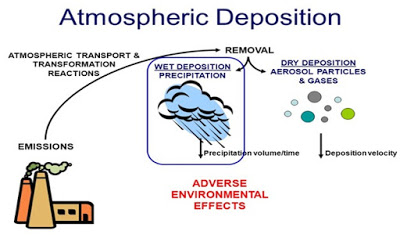
What is Ocean Acidification?
Ocean acidification
occurs due to the change in ocean chemistry which happens due to the uptake of
atmospheric chemicals like carbon, sulfur, and nitrogen. The anthropogenic
release of carbon dioxide (CO2) is the dominant cause of ocean acidification
while in several coastal areas, sulfur and nitrogen are also significant.
The ocean is a sink of Carbon:
The ocean absorbs
atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2).
Carbon capture and storage is called carbon sequestration.
Oceans capture and store carbon from the atmosphere.
Causes of Ocean Acidification:
For the past 200 years,
the rapid increase in anthropogenic atmospheric CO2, which directly leads to
decreasing ocean pH through an air-sea gas exchange, has been and continues due
to the following reasons.
The rapid increase in atmospheric CO2 in the past 200 years due to
anthropogenic activities is the leading factor in decreasing ocean pH due to
air and sea gas exchange. The primary causes of ocean acidification are as
follows.
-
Combustion of fossil fuel
-
Cutting of forest (Deforestation)
-
Industrialization
-
Production of cement
-
Land-use changes
How carbon dioxide (CO2) is the main cause of ocean acidification?
(Chemical reaction)
When CO2 dissolves in seawater, carbonic acid is produced via the
reaction:
In seawater CO2
dissolves and form carbonic acid through the reaction below:
CO2 +
H2O................................. H2CO3
The carbonic acid splits
in seawater and releases hydrogen ions and bicarbonate:
H2CO3......................................H+
+ HCO3-
The increased
concentration of hydrogen ions in seawater increases acidity in oceans.
The result of the
release of hydrogen ions in seawater is that it reacts with any carbonate ion
and forms bicarbonate.
H++ CO 32--.................................H2CO3-
The above phenomena
remove carbonate ions from seawater and it creates difficulty for aquatic
organisms to form calcium carbonate (CaCO3) which is necessary for their shell
formation.

How aquatic life affected by ocean
acidification?
The ocean acidification
affects some species of microscopic algae and calcifying plankton which
are the base of marine chain and food for larger organisms i.e. fish and
whales. The equilibrium chemical condition and pH level are important to build
calcium-based shells and other structures for many seawater organisms like
clams, mussels, sea urchins, microscopic plankton, etc. Ocean acidification
affects their growth, reproduction, and survival in such a particular
environment.
Conclusion:
The ocean acidification
will diminish the ocean's capability to capture and store atmospheric carbon
and it will severely affect marine life. If concrete steps will
not take to curb ocean acidification then its repercussions will be felt by the
global economy by disrupting the food chain.