watersoilairandnoisepollution.blogspot.com is the best website to understand basic knowledge about Environmental Pollution i.e. Air Pollution, Water Pollution, Soil pollution and Noise pollution, Greenhouse gases, Solid Waste Management etc
Wednesday, 21 April 2021
Sunday, 23 June 2019
Greenhouse Gases | Greenhouse Effect | Impact of greenhouse gases on environment
Introduction:
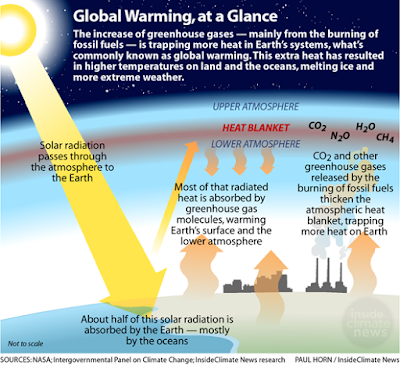
The term “greenhouse” was first used by Nils Gustaf Ekholm (Swedish meteorologist) in 1901. Greenhouse gases are surrounding the earth's atmosphere to prevent the loss of heat into outer space. These gases are essential to sustain life on earth.
The abundance of Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere due to
anthropogenic activities are dangerous to life on earth:
The global community is
facing the issue of increased concentration of greenhouse gases which have
ultimate repercussions on human life and our natural climate.
Greenhouse Gases: CO2, CH4, N2O, Water vapors, etc
The UN climate conference of Paris
agreed by I95 countries to reduce the emissions of CO2 and other greenhouse
gases. The aim was to limit the global temperature below 2 ºC (relative to
pre-industrial climate). According to Climatologists the increased
concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere due to human activities
(burning of fossil fuel and deforestation) is warming the planet earth. These
gases act in a glass of a greenhouse which allows the sunlight to enter and
prevent the heat from escaping. The rise in atmospheric temperature is directly
related to an increase in anthropogenic emissions of greenhouse gases. Water
vapors, Methane, Carbon dioxide, Nitrous oxides, Ozone, and Chlorofluorocarbon
are the most abundant greenhouse gases in the atmosphere whereas
Chlorofluorocarbon is artificial gas. It is not found naturally in the
environment. The percentage contribution of greenhouse gases includes water vapors
(36-70%), carbon dioxide (9-26%), Methane (4-9%), Ozone (3-7%).
Impact of Greenhouse Gases on Environment:
- Impact on human life
- Global Warming
- Sea level rise
- Economic Impact
- Impact on Agriculture
- Effects on Aquatic system
- Effects on Hydrological Cycle
Control Measure of Greenhouse Gases:
- Financing low carbon energy
- Clean development mechanism
- Green energy portfolio standard
Following initiatives are mandatory to reduce the effects of
greenhouse gases:
- Conservation of energy
- Use of renewable energy
- Reforestation
- Methane gas recovery from solid waste
- Banning of CFC production
- National standards of pollutants
- International conferences and seminars
Thursday, 20 June 2019
Ocean Acidification | Ocean carbon sink | Causes of Ocean Acidification
What is Ocean Acidification?
Ocean acidification
occurs due to the change in ocean chemistry which happens due to the uptake of
atmospheric chemicals like carbon, sulfur, and nitrogen. The anthropogenic
release of carbon dioxide (CO2) is the dominant cause of ocean acidification
while in several coastal areas, sulfur and nitrogen are also significant.
The ocean is a sink of Carbon:
The ocean absorbs
atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2).
Carbon capture and storage is called carbon sequestration.
Oceans capture and store carbon from the atmosphere.
Causes of Ocean Acidification:
For the past 200 years,
the rapid increase in anthropogenic atmospheric CO2, which directly leads to
decreasing ocean pH through an air-sea gas exchange, has been and continues due
to the following reasons.
The rapid increase in atmospheric CO2 in the past 200 years due to
anthropogenic activities is the leading factor in decreasing ocean pH due to
air and sea gas exchange. The primary causes of ocean acidification are as
follows.
- Combustion of fossil fuel
- Cutting of forest (Deforestation)
- Industrialization
- Production of cement
- Land-use changes
How carbon dioxide (CO2) is the main cause of ocean acidification?
(Chemical reaction)
When CO2 dissolves in seawater, carbonic acid is produced via the
reaction:
In seawater CO2
dissolves and form carbonic acid through the reaction below:
CO2 +
H2O................................. H2CO3
The carbonic acid splits
in seawater and releases hydrogen ions and bicarbonate:
H2CO3......................................H+
+ HCO3-
The increased
concentration of hydrogen ions in seawater increases acidity in oceans.
The result of the
release of hydrogen ions in seawater is that it reacts with any carbonate ion
and forms bicarbonate.
H++ CO 32--.................................H2CO3-
The above phenomena remove carbonate ions from seawater and it creates difficulty for aquatic organisms to form calcium carbonate (CaCO3) which is necessary for their shell formation.
How aquatic life affected by ocean
acidification?
The ocean acidification
affects some species of microscopic algae and calcifying plankton which
are the base of marine chain and food for larger organisms i.e. fish and
whales. The equilibrium chemical condition and pH level are important to build
calcium-based shells and other structures for many seawater organisms like
clams, mussels, sea urchins, microscopic plankton, etc. Ocean acidification
affects their growth, reproduction, and survival in such a particular
environment.
Conclusion:
The ocean acidification will diminish the ocean's capability to capture and store atmospheric carbon and it will severely affect marine life. If concrete steps will not take to curb ocean acidification then its repercussions will be felt by the global economy by disrupting the food chain.
Tuesday, 18 June 2019
Groundwater Pollution
The earth’s
97.5% water is saline and only 2.5% is fresh water and 68.9% of the freshwater
is locked in ice caps and glaciers and 29.9% of fresh water is found on the
sub-surface. In developed countries, 95%
population having access to safe drinking water and 90% population has
sufficient sanitation facilities. Almost 50% of the
groundwater used in cities is obtaining from wells, boreholes, and springs. One
fifty million population of Latin Americans and greater than 1000 million Asian
are depending on groundwater. Groundwater contamination is a very noteworthy
environmental concern of the time. Regardless of its importance, groundwater
resource is not properly managing. There are various probable sources of
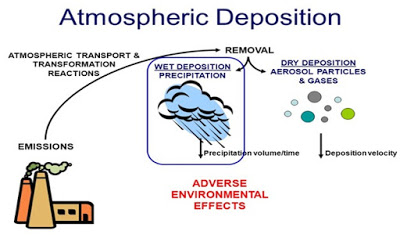
groundwater pollution in cities including point, non-point, and linear sources.
Point sources include industrial effluents, domestic sewage, and storm
overflow, non-point sources include construction work, agriculture activities,
and atmospheric deposition and linear sources are roads and sewer system. The
groundwater contamination can be resulting from leakage of sewage. Anthropogenic
activities such as agriculture, industrial, and municipality are responsible
for discharging and recharging contaminants into groundwater. The groundwater
quality deterioration resulting from leachate percolation mainly occurs during
the monsoon season and escalating the diseases related to groundwater
contamination. Groundwater contamination
occurs mostly in the vicinity of landfill and municipal waste disposal sites
and increasing the chances of percolation in aquifers. The presence
of emerging organic pollutants can be well examined and analyzed in wastewater
and surface water as compared to groundwater. Emerging organic pollutant's
major source is wastewater whereas surface water carries its maximum load.
Approximately 2.3 billion population across the world is suffering from
diseases related to polluted water. Worldwide, approximately polluted drinking
water and insufficient sanitation kill 1.6 million children below the age of
five years, and 84% of them are residing in villages. Water contamination is
the foremost health and environmental issue in Pakistan. The main sources of
groundwater pollution in Pakistan are the discharging of waste effluents into
water bodies by many industrial units including textile, fertilizers,
pesticides, steel, dying chemicals, cement, leather, etc. In Pakistan 20-40 %
of hospital beds are occupied by patients with waterborne diseases like
diarrhea, hepatitis, typhoid, dysentery, cholera, etc. One-third of all
deaths occur across the country owing to waterborne diseases. Heavy metals
present in drinking water can damage vital organs i.e. kidney, liver, and
central nervous system. They also cause abnormality in blood composition. There
is a dire need to cope with the issue by responsible authorities to protect the
health of citizens.
Sunday, 16 June 2019
Effects of Acid Rain on Plants | Effects of Acid Rain on Aquatic Life | Effects of Acid Rain on Human Health | Effects of Acid Rain on Soil | Effects of Acid Rain on Buildings
Effect on Plants:
An acid rain damage plant leaves (Necrosis). It leaches the
minerals or nutrients from the soil through surface runoff and affects the
growth and development of crops and forests.
Harmful Effects on Aquatic Life:
- Acid rain increases acidity in water bodies
- It stops the hatching of fish eggs
- It changes the population ratio of fish
- It affects the ecosystem
Effects on Human Health:
Acid
rain can cause Asthma and Bronchitis disease. In the atmosphere, both SO2 and
NOx react to form fine sulfate and nitrate particles that can be inhaled into
the lungs.
Effects on Soil:
Acid rain affects the
chemistry of soil and the availability of minerals in the soil. Nutrients
availability has a strong relation with soil pH. When the pH of water decreases
metals solubility decreases. Acid rain leaches the mineral ions through surface
runoff or it pushes deeper into the soil and finally plants roots cannot get
minerals from deeper horizons of soil which affects their growth.
Effects on the Built Environment:
Calcium carbonate is the
major component of marble and it easily reacts with sulfuric acid (transported
by acid rains) and forms calcium sulfate according to the reaction:
CaCO3 +
H2SO4 → CaSO4 + CO2 +
H2O
Calcium sulfate (CaSO4) is a thousandfold more soluble in water than Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) due to which it is easily washed out by the rain.
 |
Fig: Material removal from the artifact surfaces erases its characters. |
Acid Rain is a very
serious and dangerous issue facing the modern world. To cope with acid rain
there is a dire need to reduce gaseous emissions (burning of fossil fuel), find
alternative sources of energy, protect the resources and restore the damage
done by acid rain.
Thursday, 13 June 2019
Acid Rain | Acid Rain Definition | How is acid rain formed?
Acid Rain Definition:
Acid rain is any form of precipitation that is
unusually acidic (elevated level of hydrogen ions) due to anthropogenic gaseous
emissions in the atmosphere. Acid rain contains acidic components such as sulfuric
acid and nitric acid.
Brief History of Acid Rain:
Measuring Acid Rain: (How it can be determined if rain is acid
rain)
Acid rain is measured on
a pH scale. Acid rain is one of the most serious environmental problems that
emerged due to air pollution. Normal or unpolluted rainfall has a pH of 5.6
because carbon dioxide and water in the air react together to form carbonic
acid, a weak acid.
CO2 +
H2O............ H2CO3 (carbonic acid).
The term acid rain is applied to any type of precipitation with a pH level below 5.
Acid Rain Formation:
Acid rain is the consequence of air pollution. When moisture of air reacts with oxides of carbon, sulfur, and nitrogen in the atmosphere to produce a mixture of carbonic, sulfuric, and nitric acids.
Causes and Sources of Acid Rain:
- Anthropogenic activities are the main cause of acid rain which includes the burning of fossil fuel.
- The emission of gases from automobiles.
- Burning of coal from Power plant
- The emission of gases from industries
- Both Sulfur dioxide and Nitrogen dioxide are the major sources of acid rain formation.
Dry and Wet Deposition:
Wet deposition refers to fog, acid rain, and snow. Wet deposition of acid rain affects a variety of plants and animals. Dry deposition refers to acidic gases and particles. Almost half of the acidity in the atmosphere falls back to the ground through dry deposition.
Friday, 7 June 2019
Effects of Noise Pollution | Effects of noise pollution on human health
The effects of noise
pollution depend on the susceptibility of the individual, nature of the noise,
and duration of exposure.
The impact of noise on human health can be classified into the following
categories.
1- Auditory Health Effects
2- Non-auditory Health Effects
1- Auditory Health Effects:
Noise pollution causes hearing loss:
Hearing loss results from prolonged exposure to high noise levels.
Reduced hearing sensitivity: Exposure to occupational noise can significantly
reduce hearing sensitivity.
2- Non-auditory Health Effects:
Non-auditory health effects of noise
pollution are as following:
1- Mental Health
Effects
2- Sleep Disturbances
3- Hypertension
4- Low Performance
5- Cardiovascular and Physiological Effects
1- Mental Health
Effects:
Noise in the industry can
be a direct cause of general health problems. It can create conditions of
psychological stress, which can in turn cause physiological stress reactions.
2- Sleep
Disturbances:
It has been found that
more sleeping medicines are consumed by people living in noisy areas than in
quieter areas.
3- Hypertension:
Prolonged exposure to
high-intensity industrial noise increases the risk of hypertension.
4- Low Performance:
Workers in the industry
with high noise levels show slightly lower productivity than those in
departments with lower noise exposure.
5- Cardiovascular and
Physiological Effects:
High levels of noise are associated with
a high risk of physiological changes such as hypertension, increased levels of
heartbeat rate.
Aircraft noise exposure was related to
more medical treatment for heart trouble and hypertension.
Waste | Definition of Waste | Types of Waste | Sources of Waste
Definition: Waste (also known as rubbish, trash, refuse, garbage, junk) is any unwanted or useless materials. Waste is any substance that is...

-
1) Impacts on Human Health: Microbial contamination in water bodies causes diseases like cholera, dysentery, diarrhea, polio, typhoid, hep...
-
Definition: The presence of gases, liquids, and solids in the atmosphere in high enough levels that can harm different components of the e...
-
Based on origin, air pollution can be categorized into natural and anthropogenic (man-made) sources. Natural Sources of Air Pollution: Exam...